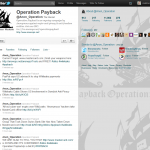
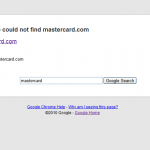
Just as I was getting my head around the whole WikiLeaks issue and where I stand, this happens…
The website of MasterCard has been hacked and partially paralysed in apparent revenge for the international credit card’s decision to cease taking donations to WikiLeaks.
A group of online activists calling themselves Anonymous appear to have orchestrated a DDOS (“distributed denial of service”) attack on the site, bringing its service at www.mastercard.com to a halt for many users.
“Operation: Payback” is the latest salvo in the increasingly febrile technological war over WikiLeaks. MasterCard announced on Monday that it would no longer process donations to the whistleblowing site, claiming it was engaged in illegal activity.
The group, which has been linked to the influential internet messageboard 4Chan, has been targeting commercial sites which have cut their ties with WikiLeaks. The Swiss bank PostFinance has already been targeted by Anonymous after it froze payments to WikiLeaks, and the group has vowed to target Paypal, which has also ceased processing payments to the site. Other possible targets are EveryDNS.net, which suspended dealings on 3 December, Amazon, which removed WikiLeaks content from its EC2 cloud on 1 December, and Visa, which suspended its own dealings yesterday.
The action was confirmed on Twitter at 9.39am by user @Anon_Operation, who later tweeted: “WE ARE GLAD TO TELL YOU THAT http://www.mastercard.com/ is DOWN AND IT’S CONFIRMED! #ddos #wikileaks Operation:Payback(is a bitch!) #PAYBACK”
No one from MasterCard could be reached for immediate comment, but a spokesman, Chris Monteiro, has said the site suspended dealings with WikiLeaks because “MasterCard rules prohibit customers from directly or indirectly engaging in or facilitating any action that is illegal”.
DDOS attacks, which often involve flooding the target with requests so that it cannot cope with legitimate communication, are illegal.
guardian.co.uk © Guardian News & Media Limited 2010
Published via the Guardian News Feed plugin for WordPress.