The last several weeks I’ve been working on a new project, a SoLoMo initiative, as John Doerr or Mary Meeker would call it.

It’s a mobile publishing platform that resembles a community notice board. Â It’s called n0tice*:
After seeing Google’s “News near you” service announced on Friday I thought it was a good time to jump into the conversation and share what I’m up to. Â Clearly, there are a lot of people chasing the same or similar issues.
First, here’s some background. Â Then I’ll detail what it does, how it works, and what I hope it will become.
What is n0tice?
It began as a simple hack day project over a year ago. Â I was initially just curious about how location worked on the phone. Â At first I thought that was going to be beyond me, and then Simon Willison enlightened me to the location capabilites inherent in modern web browsers. There are many solutions published out there. Here’s one.
It took half a second from working out how to identify a user’s location to realizing that this feature could be handy for citizen reporters.
Around the same time there was a really interesting little game called noticin.gs going around which was built by Tom Taylor and Tom Armitage, two incredibly talented UK developers. Â The game rewarded people for being good at spotting interesting things in the world and capturing a photo of them.
Ushahidi was tackling emergency response reporting. And, of course, Foursquare was hitting its stride then, too.
These things were all capturing my imagination, and so I thought I would try something similar in the context of sharing news, events and listings in your community.

However, I was quite busy with the Guardian’s Open Platform, as the team was moving everything out of beta, introducing some big new services and infusing it into the way we operate. Â I learned a lot doing that which has informed n0tice, too, but it was another 12 months before I could turn my attention back to this project. Â It doesn’t feel any less relevant today than it did then. It’s just a much more crowded market now.
What does n0tice do?
The service operates in two modes – reading and posting.
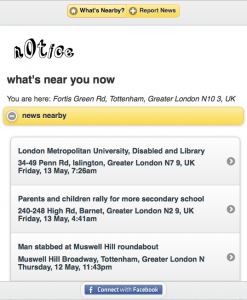 When you go to n0tice.com it will first detect whether or not you’re coming from a mobile device. Â It was designed for the iPhone first, but the desktop version is making it possible to integrate a lot of useful features, too.
When you go to n0tice.com it will first detect whether or not you’re coming from a mobile device. Â It was designed for the iPhone first, but the desktop version is making it possible to integrate a lot of useful features, too.
(Lesson:  jQuery Mobile is amazing. It makes your mobile projects better faster. I wish I had used it from day one.)
It will then ask your permission to read your location. Â If you agree, it grabs your latitude and longitude, and it shows you what has been published to n0tice within a close radius.
(Lesson: It uses Google Maps and their geocoder to get the location out of the browser, but then it uses Yahoo!’s geo services to do some of the other lookups since I wanted to work with different types of location objects. Â This combination is clunky and probably a bad idea, but those tools are very robust.)
You can then zoom out or zoom in to see broader or more precise coverage.
Since it knows where you are already, it’s easy to post something you’ve seen near you, too. Â You can actually post without being logged in, but there are some social incentives to encourage logged in behavior.
Like Foursquare’s Mayor analogy, n0tice has the ‘Editor’ badge.
The first person to post in a particular city becomes the Editor of that city. Â The Editor can then be ousted if someone completes more actions in the same city or region.
It was definitely a challenge working out how to make sensible game mechanics work, but it was even harder finding the right mix of neighborhood, city, country, lat/long coordinates so that the idea of an ‘Editor’ was consistent from place to place.
London and New York, for example, are much more complicated given the importance of the neighborhoods yet poorly defined boundaries for them.
(Lesson: Login is handled via Facebook. Their platform has improved a lot in the last 12 months and feels much more ‘give-and-take’ than just ‘take’ as it used to. Now, I’m not convinced that the activities in a person’s local community are going to join up naturally via the Facebook paradigm, so it needs to be used more as a quickstart for a new service like this one.)
The ‘Editor’ mechanics are going to need a lot more work. Â But what I like about the ‘Editor’ concept is that we can now start to endow more rights and priveleges upon each Editor when an area matures.
Perhaps Editors are the only ones who can delete posts. Perhaps they can promote important posts. Maybe they can even delegate authority to other participants or groups.
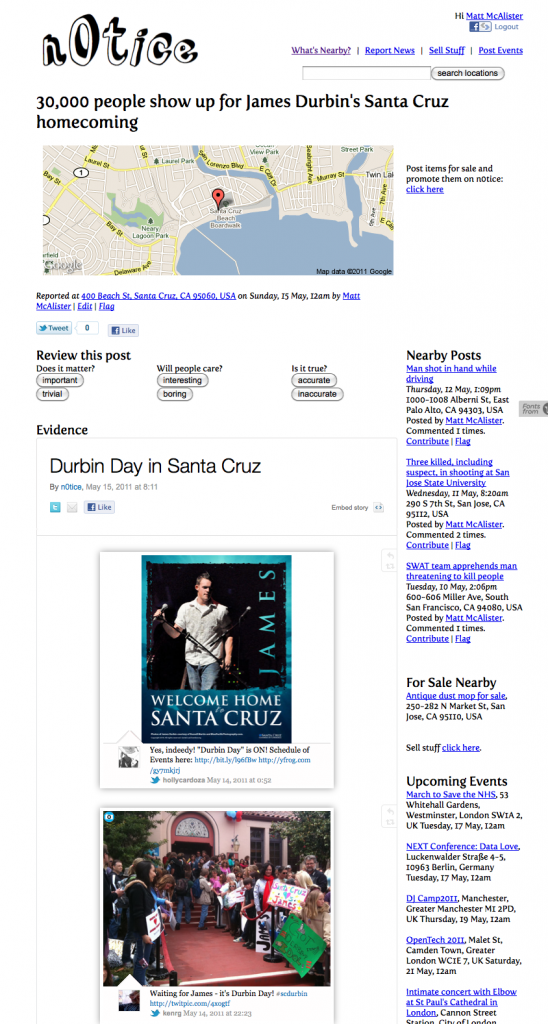 Of course, quality is always an issue with open communities. Having learned a few things about crowdsourcing activities at the Guardian now, there are some simple triggers in place that should make it easier to surface quality should the platform scale to a larger audience.
Of course, quality is always an issue with open communities. Having learned a few things about crowdsourcing activities at the Guardian now, there are some simple triggers in place that should make it easier to surface quality should the platform scale to a larger audience.
For example, rather than comments, n0tice accepts ‘Evidence’.
You can add a link to a story, post a photo, embed a video or even a storify feed that improve the post.
Also, the ratings aren’t merely positive/negative. Â They ask if something matters, if people will care, and if it’s accurate. That type of engagement may be expecting too much of the community, but I’m hopeful it will work.
Of course, all this additional level of interactivity is only available on the desktop version, as the mobile version is intended to serve just two very specific use cases:
- getting a snapshot of what’s happening near you now
- posting something you’ve seen quickly and easily
How will n0tice make money?
Since the service is a community notice board, it makes sense to use an advertising model that people already understand in that context: classifieds.
Anyone can list something on n0tice for free that they are trying to sell. Â Then they can buy featured promotional positions based on how large the area is in which they want their item to appear and for how long they want it to be seen there.
(Lesson: Integrating PayPal for payments took no time at all. Their APIs and documentation feel a little dated in some ways, but just as Facebook is fantastic as a quickstart tool for identity, PayPal is a brilliant quickstart for payments.)
Promotion on n0tice costs $1 per 1 mile radius per day. That’s in US dollars.
While still getting the word out and growing the community $1 will buy you a featured spot that lasts until more people come along and start buying up availability.
But there’s a lot we can do with this framework.
For example, I think it would make sense that a ‘Publisher’ role could be defined much like the ‘Editor’ for a region.
Perhaps a ‘Publisher’ could earn a percentage of every sale in a region. Â The ‘Publisher’ could either earn that privelege or license it from us.
I’m also hopeful that we can make some standard affiliate services possible for people who want to use the ad platform in other apps and web sites across the Internet. Â That will only really work if the platform is open.
How will it work for developers and partners?
The platform is open in every way.
There are both read and write APIs for it. Â The mobile and desktop versions are both using those APIs, in fact.
The read API can be used without a key at the moment, and the write API is not very complicated to use.
So, for example, here are the 10 most recent news reports with the ‘crime’ tag in machine-readable form:
http://n0tice.com/api/readapi-reports.php?output=xml&tags=crime&count=10
The client code for the mobile version is posted on Github with an open license (we haven’t committed to which license, yet), though it is a few versions behind what is running on the live site. Â That will change at some point.
And the content published on n0tice is all Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike so people can use it elsewhere commercially.
The idea in this approach to openness is that the value is in the network itself, the connections between things, the reputation people develop, the impact they have in their communities.
The data and the software are enablers that create and sustain the value. Â So the more widely used the data and software become the more valuable the network is for all the participants.
How scalable is the platform?
The user experience can scale globally given it is based on knowing latitude and longitude, something treated equally everywhere in the world. Â There are limitations with the lat/long model, but we have a lot of headroom before hitting those problems.
The architecture is pretty simple at the moment, really. Â There’s not much to speak of in terms of directed graphs and that kind of thing, yet. Â So the software, regardless of how badly written it is, which it most definitely is, could be rewritten rather quickly. Â I suspect that’s inevitable, actually.
The software environment is a standard LAMP stack hosted on Dreamhost which should be good enough for now. Â I’ve started hooking in things like Amazon’s CloudFront, but it’s not yet on EC2. Â That seems like a must at some point, too.
The APIs should also help with performance if we make them more cacheable.
The biggest performance/scalability problem I foresee will happen when the gaming mechanics start to matter more and the location and social graphs get bigger. Â It will certainly creak when lots of people are spending time doing things to build their reputation and acquire badges and socialize with other users.
If we do it right, we will learn from projects like WordPress and turn the platform into something that many people care about and contribute to. Â It would surely fail if we took the view that we can be the only source of creative ideas for this platform.
To be honest, though, I’m more worried about the dumb things like choking on curly quotes in users’ posts and accidentally losing users’ badges than I’m worried about scaling.
It also seems likely that the security model for n0tice is currently worse than the performance and scalability model. The platform is going to need some help from real professionals on that front, for sure.
What’s the philosophy driving it?
There’s most definitely an ideology fueling n0tice, but it would be an overstatement to say that the vision is leading what we’re doing at the moment.
In its current state, I’m just trying to see if we can create a new kind of mobile publishing environment that appeals to lots of people.
There’s enough meat to it already, though, that the features are very easy to line up against the mission of being an open community notice board.
Local UK community champion Will Perrin said it felt like a “floating cloud of data that follows you around without having to cleave to distribution or boundary.”
I really like that idea.
Taking a wider view, the larger strategic context that frames projects like this one and things like the Open Platform is about being Open and Connected. Â Recently, I’ve written about Generative Media Platforms and spoken about Collaborative Media. Â Those ideas are all informing the decisions behind n0tice.
What does the future look like for n0tice?
The Guardian Media Group exists to deliver financial security for Guardian News and Media.
My hope is that we can move n0tice from being a hack to becoming a new GMG business that supports the Guardian more broadly.
The support n0tice provides should come in two forms: 1) new approaches to open and collaborative journalism and 2) new revenue streams.
It’s also very useful to have living projects that demonstrate the most extreme examples of ‘Open and Connected‘ models. Â We need to be exploring things outside our core business that may point to the future in addition to moving our core efforts where we want to go.
We spend a lot of time thinking about openness and collaboration and the live web at the Guardian. Â If n0tice does nothing more than illustrate what the future might look like then it will be very helpful indeed.
However, the more I work on this the more I think it’s less a demo of the future and more a product of the present.
Like most of the innovations in social media, the hard work isn’t the technology or even the business model.
The most challenging aspect of any social media or SoLoMo platform is making it matter to real people who are going to make it come alive.
If that’s also true for n0tice, then the hard part is just about to begin.
* The hack was originally called ‘News Signals’. Â But after trying and failing to convince a few people that this was a good idea, including both technical people and potential users, such as my wife, I realized the name really mattered.
I’ve spent a lot of time thinking about generative media platforms, and the name needed to reflect that goal, something that spoke to the community’s behaviors through the network. It was supposed to be about people, not machines.
Now, of course, it’s hard to find a short domain name these days, but digits and dots and subdomains can make things more interesting and fun anyhow. Luckily, n0tice.com was available…that’s a zero for an ‘o’.

 There must be kitchen design experts around the world I can learn from. Equally, I’m sure there is a guy around the corner from me who can give me some tips on local services. Will Architectural Digest or Home & Garden connect me to these different people? No. Will The San Francisco Chronicle connect us? No.
There must be kitchen design experts around the world I can learn from. Equally, I’m sure there is a guy around the corner from me who can give me some tips on local services. Will Architectural Digest or Home & Garden connect me to these different people? No. Will The San Francisco Chronicle connect us? No.


 But the problem isn’t the research, it’s the product roadmap. In order to deliver a big punch in the market and cut through the noise, you need to be bold. And big changes that get noticed by big audiences require a lot of planning and complicated scheduling. Big changes are expensive on many levels.
But the problem isn’t the research, it’s the product roadmap. In order to deliver a big punch in the market and cut through the noise, you need to be bold. And big changes that get noticed by big audiences require a lot of planning and complicated scheduling. Big changes are expensive on many levels. At the risk of invalidating everything I’ve said here by quoting a man who’s social and political beliefs go against just about everything I believe,
At the risk of invalidating everything I’ve said here by quoting a man who’s social and political beliefs go against just about everything I believe, 
 I used to attend a charity event called
I used to attend a charity event called 


